A bacterial infection is accompanied by severe inflammation and purulent discharge (exudate). No application antibacterial drugs it is impossible to overcome the disease. Antibiotics are an effective tool in the fight against microorganisms. Eye drops based on antibiotics, they are used to treat diseases of the eye and its appendages.
Infectious eye lesions can be cured through the use of bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs.
In ophthalmology, antibiotics belonging to different groups are used:
To the list of antibacterial ophthalmic agents includes drugs from the list:
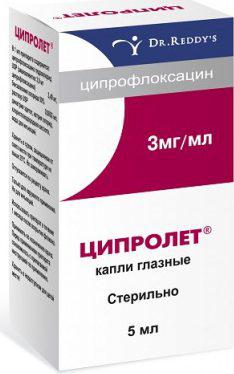
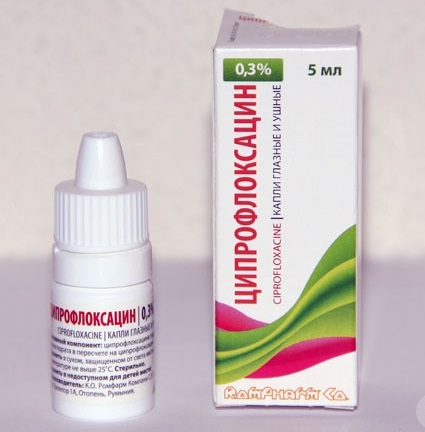
During treatment with eye drops based on Tsiprolet, contact lenses should not be used. After instillation, temporarily limit work at heights and driving. The periods between administration of the drug increase, reducing the daily dose. Possible side effects: redness of the eyes, itching, swelling of the eyelids.
Indications:
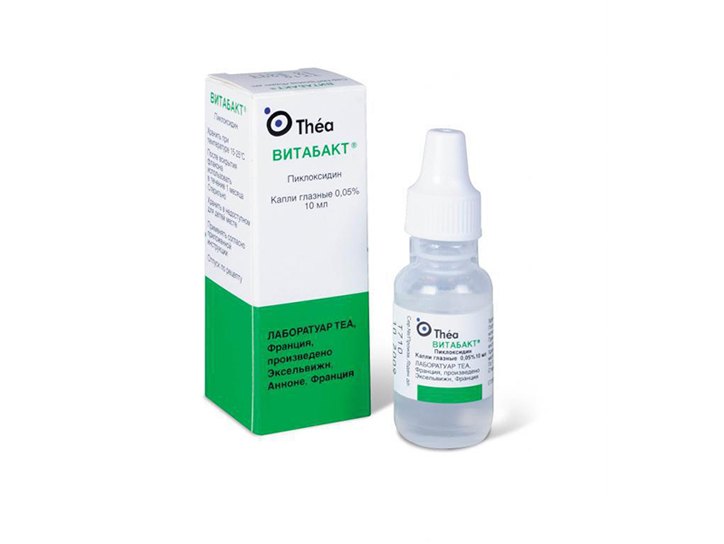
Dacryocystitis occurs congenital in 1% of newborns. The cause of the disease is a violation of the patency of the tear ducts. WITH The accumulation of tear fluid in the lacrimal sac leads to the development of inflammation. Floxal has no contraindications for children infancy. Therapy with Ofloxacin in combination with massage of the lacrimal sac allows you to do without surgical intervention.
Purpose:
Toxic. Contraindicated during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and children under one year of age.
Main feature when using ophthalmic steroid drugs– this is an increase in the period between instillation when the condition improves, and thus a decrease daily dose medicines.
At the beginning of therapy, drops are administered 1-2 drops every 2 hours. After 2-3 days, the interval between procedures is set to 4-6 hours.
Hormonal eye drops are prescribed when other medications do not help. The main active ingredient is the synthetic glucocorticosteroid Dexamethasone. The steroid solution penetrates the mucous membrane of the eye, affecting the site of inflammation at the cellular level. In this case, there is no inflammatory reaction to its use.
Hormonal drops are ineffective in the treatment of inflammatory phenomena caused by bacterial, viral, fungal infections, glaucoma and corneal erosion. Long-term use of hormonal drops (over 14 days) can cause cataracts and glaucoma.
For children hormonal drugs are prescribed no earlier than 7 years (Lotoprednol), with strict adherence to the procedure. Because of the possibility of such complications, all forms medicines are not prescribed to pregnant women.
The positive quality of Dexamethasone is the main side effect when using drugs based on it. As a result of long-term therapy, immunity decreases. The period of use of hormonal drops does not exceed 10-14 days.
The combination of the properties of antibiotics and hormones in one drug enhances the effectiveness antibacterial therapy. The side effects of antibiotics and hormones persist in combination eye drops.
Eye drops containing antibiotics and hormones:
Eubetal. Compound:
A combination of three antibiotics allows you to have a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect on gram-positive, gram-negative bacteria, chlamydia, and mycoplasma. GCS is an effective anti-inflammatory agent.
Does not apply:
Side effects: burning and tingling in the eye.
The general requirement for treatment with combined eye drops is to remove contact lenses to administer the medication and put them back on after 15-20 minutes. Reason: the possibility of fluid accumulation on the cornea, resulting in an overdose.
Eye drops are produced on the basis of antibiotics, hormones and in combined form. To suppress bacterial infection antibiotic solutions are used. Hormonal drops help eliminate non-infectious inflammatory phenomena. Combination drugs combine positive properties hormones and antibiotics. Purpose of combined eye drops- treatment of severe cases of microbial infection with inflammation.
– drugs that are in first place in terms of frequency of use in ophthalmological practice. Regardless of the etiology of the inflammatory disease ( fungal infection, viruses or pathogenic bacteria), it is impossible to cure it without the type of drops in question. Yes, the symptoms will become less intense, the patient may even talk about recovery even after using some folk remedies. Actually cure inflammatory process, avoid complications and not introduce pathology into chronic form course is possible only with the help of antibacterial therapy.
Almost all known groups of antibiotics are used in ophthalmic practice:
All of them have a powerful bactericidal and antibacterial effect, are addictive and are suitable for destroying a specific pathogenic microorganism. That is why antibacterial eye drops can only be prescribed by a doctor - he will take into account the patient’s age, general health, the presence of chronic liver and kidney diseases, and the ophthalmological diagnosis.
The most popular and frequently used drugs in question include:
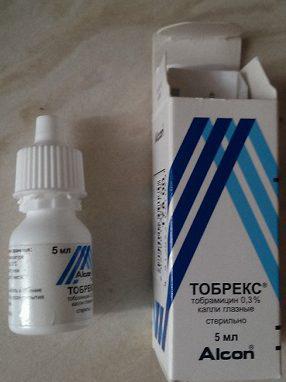
These antibiotic eye drops have an aggressive effect on pathogenic microorganisms, are broad-spectrum agents and are used to treat any inflammatory diseases organs of vision. Tobrex can also be used in pediatric practice; it is often used to treat eye pathologies even in newborns, but with mandatory supervision by a specialist.
These eye drops may cause side effects, and in this case, patients will complain of pain and burning in the eyes, slight swelling of the eyelids. As a rule, this is not a reason to cancel treatment, especially since general course therapy is short - no more than 5-7 days.
For adults, instill 2 drops into each eye at least 4 times and no more than 6 times a day. Literally on the second day, all symptoms of the disease disappear, but this does not mean that treatment can be interrupted - the course prescribed by the ophthalmologist must be completely followed. Eye drops for children are prescribed in a dosage of 1 drop in each eye 3 times a day.
One of the most harmless eye drops with an antibacterial effect - they can be used to treat an infectious or inflammatory disease even during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is this drug that is actively used in maternity hospitals for the treatment of conjunctivitis in newborns.
Sulfacyl sodium is available in the form of a 10/20/30% solution. The dosage for an adult is 2 drops in each eye no more than 6 times a day; for a child of any age, the number of procedures for instilling the drug is determined by the doctor.
 Levomycetin eye drops are used to treat both adults and children.
Levomycetin eye drops are used to treat both adults and children. Antibacterial eye drops wide range actions are used to treat any inflammatory eye diseases. It is also prescribed for the treatment of children with blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis. Often, after use, patients note the appearance of burning, pain and itching in the organs of vision - this does not mean that it is necessary to cancel therapy and select another drug. Usually after 2-3 instillations everything discomfort pass.
Considered medicinal product instill 1 drop into each eye 3-4 times a day. If you are going to treat a child, you should consult your doctor about the dosage of Levomycetin. The duration of treatment is a maximum of 7 days, but if there is no improvement in the condition on days 3-4, then you should inform your ophthalmologist and try to change the drug.
This drug is more often used in ENT practice, but ophthalmologists also prescribe it to their patients. The antibiotic copes well with aggressive infection and severe inflammation, quickly relieves the patient of such unpleasant symptoms as redness, itching, profuse lacrimation, and purulent discharge. Normax is also used to treat diseases of the organs of vision caused by the chlamydia agent.
Doctors prescribe this drug to be dropped into the eyes every hour, 1 drop. Then, when the acute manifestation of the symptoms of the pathology is removed, the dosage is adjusted downward - 1 drop in each eye 3 times a day until complete recovery.
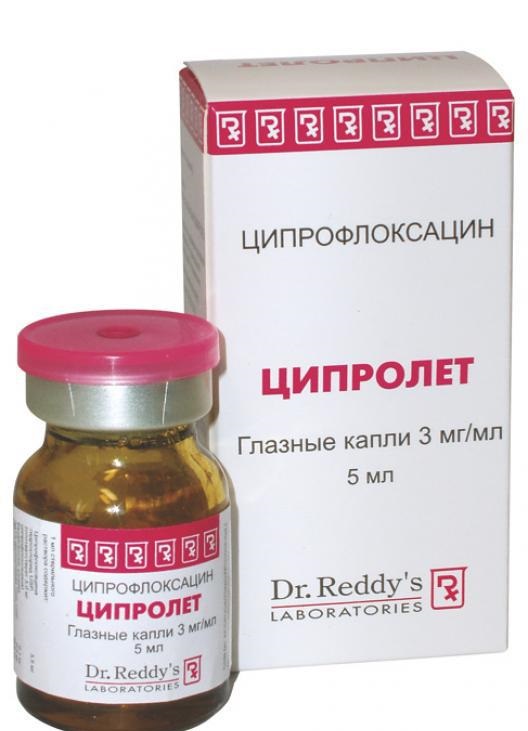
A product with a broad-spectrum antibiotic, used to treat chronic and acute inflammatory and infectious diseases of the organs of vision. In addition, if eye surgery was performed, then this remedy is excellent for preventing postoperative infection. These eye drops are not prescribed for children, as they are highly toxic, enter the general bloodstream and can lead to problems with the liver and kidneys. For the same reason, Tsipromed is not used for the treatment of ophthalmic pathologies in pregnant and lactating women.
If the disease is acute, then this drug is instilled into the eyes at least 8 times a day. Only after the acute phase of the disease has passed, the dosage is reduced to 1 drop in each eye 2-3 times a day. In case of treatment chronic disease during an exacerbation, Tsipromed is used 2 drops in each eye 3-4 times a day.
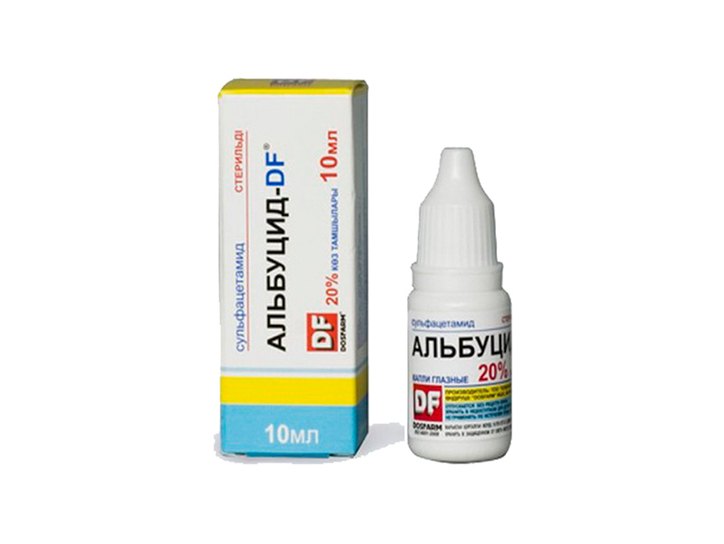
This is perhaps the most famous drug used in ophthalmic practice. It is used to treat the most various diseases eye, he proved himself to be an excellent remedy for conjunctivitis, blepharitis. Albucid is also used as a prophylactic agent in the postoperative period - this helps to avoid the progression of the infectious process.
Albucid does not penetrate into the bloodstream and does not have any toxic effect on the body, therefore it is actively used in pediatric practice. This drug They are also used for instillation of newborns - this is done literally immediately after the birth of the child to avoid the development of a purulent infection.
When treating inflammatory or infectious diseases of the organs of vision, it is not enough to receive competent prescriptions from an ophthalmologist! Certain rules must be followed for therapy to be truly effective:
Antibacterial eye drops often cause allergic reaction, which can manifest itself as itching and redness, swelling of the eyelids, peeling of the skin around the eyes, and excessive lacrimation. In this case, the course of therapy should be stopped and you should consult your ophthalmologist. Most likely, the drug will be replaced.
Antibiotic eye drops may cause an increase in intraocular pressure. This condition will manifest itself as a severe headache, a feeling of fullness in the eyes, and fatigue in them. Such symptoms are a reason to immediately stop treatment and seek qualified medical help.
Antibacterial drugs are often used in ophthalmology and are always successful. In order not to make a mistake in choosing a specific product and to know the exact dosage, you should seek help from a doctor. Compliance with the recommendations for the use of the drugs in question, exact compliance with the prescribed dosages and full duration of therapy in 98% of cases lead to complete recovery.
When eye diseases are infectious, viral or fungal in nature, it is difficult to do without antibacterial therapy. After all, thanks to such medications it is possible to overcome pathogenic microorganisms.
Without the use of antibiotics, it is difficult to achieve final recovery, and sometimes a progressive situation can be aggravated even further.
Nowadays, antibacterial eye drops act directly on the site of the lesion, but everything happens gently and without manifestation adverse reactions.
Antibacterial eye drops can only be used in certain situations. These include:
Antibacterial drops should be used only after consulting a doctor. After all, only an ophthalmologist can determine the dosage of the drug and duration healing process. Interactions with other medications should also be taken into account, since if the active substance is overdosed or does not interact with other components, allergic manifestations or adverse reactions may occur.
If you need to select antibacterial drops for children, then in such a situation you need not only to visit an ophthalmologist, but also undergo a full diagnosis to determine the nature pathological process, individual intolerance and susceptibility to the active ingredients. Children's remedy should be as effective as possible, but at the same time gentle and not cause adverse reactions.
The list of antimicrobial drugs that can be used for both children and adults includes the following drops.

These include the following.
The choice of antibacterial drugs is quite large. But it is worth remembering that this type of medication can only be prescribed by a doctor, especially when it comes to children. You also need to take into account the fact that antibacterial drops may have one active ingredient, but they differ in price and adverse reactions.
Antibiotic eye drops are very effective medications. They are used to combat eye diseases caused by infection. As a rule, bacteria are the causative agents of many eye diseases, such as:
A fairly large list of ailments makes antibiotic drops very common. They occupy the largest group of medications for the eyes. According to the active substance, such medications are divided into drops with sulfonamide substances and medications with antibiotics.
Antibiotic drops are medicines in ophthalmology that contain active ingredients semi-synthetic or natural origin. They have a detrimental effect on microorganisms.
IN medical practice specialists use from different groups antibiotic eye drops, their list is as follows:
As for the second group of drugs with antibacterial effect, sulfonamide drugs, they began to be used in medical practice a little earlier, but are still actively used. Among them is such a well-known drug as, and others. They have a detrimental effect on bacteria and help get rid of infectious diseases. 
In pediatric ophthalmology, antibiotics and eye drops for children for conjunctivitis are also actively prescribed, they are used 5-7 times a day, they are very effective in treating it. Treatment of keratitis, which is very rarely observed in children, is carried out using the same methods as in adults. 
For conjunctivitis, drugs such as Trimethoprim and sodium sulfacetamide are usually used. They have no significant side effects and are relatively affordable. And the use of drugs such as aminoglycosides in the treatment of childhood diseases is only possible for a short time, since long-term use damages the corneal epithelium. The use of Neomycin can provoke contact allergies in a child. A drug such as Amikacin was developed not so long ago; it is less toxic and more suitable for instillation in children's eyes. In relation to strains that are resistant to tobramycin and gentamicin, this drug is very effective.
 During treatment bacterial conjunctivitis Erythromycin 0.5% is used in children. Povidone 2.5% is also effective. Sometimes broad-spectrum drugs are used to treat childhood diseases; they usually serve as an addition to antibacterial drugs.
During treatment bacterial conjunctivitis Erythromycin 0.5% is used in children. Povidone 2.5% is also effective. Sometimes broad-spectrum drugs are used to treat childhood diseases; they usually serve as an addition to antibacterial drugs.
For children over one year of age, Moxifloxacin 0.5% can be used to treat infections caused by Haemophilus and Chlamydia. This drug is dripped 3 times a day and has a very effective effect. However, there are certain limitations in its use.
To treat eye diseases in adults, doctors use various drops that contain antibiotics.
When prescribing the drug, the ophthalmologist is guided by the following factors:
Despite the large selection of drugs that exist today to combat eye infectious diseases, their range for the patient is significantly narrowed due to contraindications. Such contraindications, for example, may include severe liver disease, neuritis auditory nerve and others. In many cases for effective treatment broad-spectrum antibiotic eye drops are prescribed, for example, to treat keratitis.
Important! Only a doctor should prescribe eye drops with antibiotics, because such medications have a number of contraindications!
Among other things, it is very important to consider individual tolerance substances in drugs by patients. If you do not take this into account, the condition may worsen. The manifestation of allergic reactions is also possible. 
It is also very important for the effective treatment of infectious eye diseases to prescribe those drugs that are effective in combating a particular disease. If the drug causes a burning sensation in the eyes or pain, then you need to ask the doctor to choose another medicine that will be more comfortable to use. Thus, only a doctor can prescribe an effective and safe medicine for every patient.
To summarize, it should be said that today pharmacists present us with a fairly wide range of medical supplies to combat infectious eye diseases. They contain antibiotics created semi-artificially or using natural basis. In each specific case, only a specialist can prescribe this or that drug.
Redness and suppuration of the eyes, “stye” that appears on the inside or outside of the eyelids – unpleasant symptoms disorders in the child's body. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctivitis), inflammation of the ciliary margin (blepharitis), inflammation of the glands cartilage tissue century (meibomitis) and many other diagnoses usually involve treatment with antibiotics.
Antimicrobial agents may be the basis for such treatment. local action– drops, ointments, gels. They can, but they won't necessarily. What eye drops can be used in children in what cases?
![]()

All antibiotics, as their name suggests, exist to resist bacteria, microbes, and rods. If eye inflammation in a child is caused by a viral infection, antibiotics are not necessary. They will not be able to help, because... They don't know how to fight viruses. But they can cause harm, because no one has yet canceled the serious side effects of antibacterial therapy. And this includes dysbacteriosis, thrush, and decreased immunity.
In adults, eye inflammation is almost always caused by viruses. But for children it’s different - the share viral diseases equal to the proportion of bacterial ones.
Babies are actively exploring the world, they try to touch everything with their hands, and then rub their eyes with these hands... As a result, bacteria penetrate into the beneficial moist and warm environment - human eye, and the inflammatory process begins.
Even if the baby initially fell ill with the flu or ARVI, conjunctivitis can also become a bacterial complication. viral infection. To a body weakened by the flu, all kinds of harmful bacteria usually they “stick” quite willingly and quickly.
So, the most common childhood eye diseases for which antibacterial therapy can be prescribed:
These and a range of other eye diseases in children are usually provoked by Koch-Wicks bacillus, pneumococci, staphylococci, streptococci, and atypical chlamydia.

For conjunctivitis. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye is a frequent companion colds. If the disease was caused by bacteria, and not viruses, enteroviruses or allergens, then antibiotic drops will be the main component of the treatment regimen. Bacterial inflammation is easy to recognize - by purulent discharge grey-green color from the corner of the eye, sticking eyelashes, clouding of the eye.
Conjunctivitis may go away on its own without specific treatment. But any doctor will tell you that the healing process will go much faster if you start using antibiotic drops.
For blepharitis. If the cause of inflammation of the eyelash edge lies in the proliferation of bacteria, the doctor will also recommend antibiotics. Most often, these are complex drops that contain erythromycin, tetracycline, and gentamicin.
From barley. This acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle usually provokes Staphylococcus aureus. How can mothers not treat stye for their children? AND boiled egg, and a burdock compress, and grandmother’s spells... The doctor is unlikely to advise you at least one of the above. The medical approach to the disease will be simpler - drops or ointment with antibiotics. After all, barley, which is familiar to everyone, often ends with inflammation of the eye socket, lining of the brain and surgery. Especially if the abscess is heated or wetted.
For keratitis. Inflammation of the cornea is most often caused by staphylococci and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. For treatment, doctors strongly recommend taking the antibiotics Levofloxacin and Moxifloxacin.

Instilling an antibiotic into sore eye, we are reducing the load on children's body. After all, active antimicrobial substances begin their “work” immediately. The antibiotic will wear off gastrointestinal tract, the risk of dysbacteriosis and allergies is minimized.
To treat viral eye inflammation, the doctor will prescribe individual or complex drops with antiviral effect, with an anti-inflammatory drug or with hormones, and for allergic eye inflammation - drops with dexamethasone.